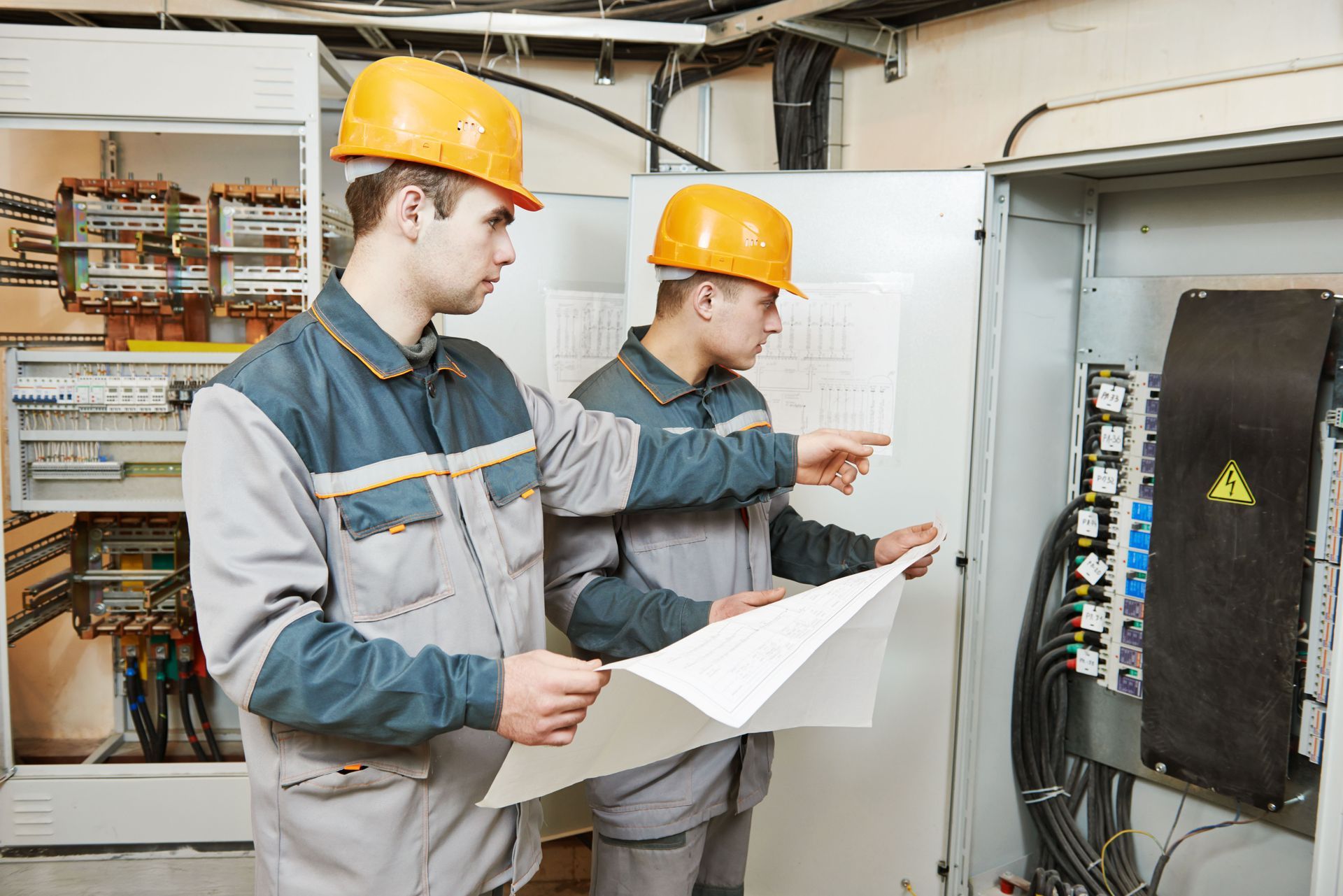
How to put out an electrical fire
January 22, 2024
Electrical Fire! How to put it out!
To keep your family safe, here are some tips to help fight an electrical fire. Knowing how to put out a small electrical fire could save you from a disaster. National estimates
for 2021 show there were almost 300 deaths and 900 injuries due to electrical malfunction fires.
If there is an electrical fire, here are some tips to extinguish it.
Turn off the power immediately .
If you can find the device that is the source of the electrical fire and safely able to unplug the cord, do so.
Do not use water to put out the fire.
Water conducts electricity. Adding water to an electrical fire can cause you to get shocked or spread the fire by conducting electricity throughout the room.
Add baking soda
If the fire is small, you may be able to smother the flame with baking soda.
Use the right fire extinguisher
Most residential fire extinguishers are classed ABC. These types of extinguishers are multi-purpose. Class C fires are the electrical fires. You need to make sure if you are using a fire extinguisher, it is labeled with C or ABC. You do not want to be using the wrong type of extinguisher for an electrical fire.
Everyone should have a fire extinguisher that is easily accesible and kept up to date to ensure proper function in your home.
Here you can find more information on fire extinguishers and purchase one for your home.
If you can’t put out the electrical fire with those steps above:
1. Leave the room. Do not stay and try to fight the fire.
2. If the fire is in a room with a door, close it to contain the fire.
3. Call 911 as soon as you are safe to do so.
4. Let the firefighters put out the flames and get your home safe.
Knowing how to put out an electrical fire is important, but we also need to take steps to prevent them from happening in the first place. Read our last blog
about winter electrical safety.


Every time a circuit breaker trips in your home, it’s doing something incredibly important—protecting you and your electrical system from danger. But have you ever wondered where these little safety devices came from, or how we protected homes before they existed? Here’s a quick look at the evolution of electrical breakers, and why they’re one of the most important inventions in modern electrical safety. ⚙️ Before Breakers: The Age of Fuses (Late 1800s – Early 1900s) Before circuit breakers became common, homes used fuses to prevent electrical overloads. A fuse contains a thin wire that melts when too much current flows through it, stopping the circuit. The problem? Once a fuse blows, it has to be replaced—every single time. Fuses worked, but they were: Inconvenient Easy to install incorrectly Prone to over-fusing (dangerously replacing with a higher-rated fuse) ⚡ Enter the Breaker: Early 20th Century Innovation The concept of the resettable circuit breaker emerged in the early 1900s, offering a reusable, more reliable solution. The first patent for a circuit breaker came in 1924 by Hugo Stotz (working with Siemens), whose design used a bimetallic strip to detect overcurrent. Breakers gained popularity throughout the 1930s–50s, especially in industrial and commercial buildings. Why they caught on: Could be reset instead of replaced More precise at detecting electrical faults Better suited for growing electrical demands 🏠 Breakers in the Modern Home (1960s–Present) By the 1960s and 70s, circuit breakers became the standard in new residential construction across the U.S. and many parts of the world, replacing fuse boxes entirely. Modern home panels include: Standard breakers – for basic overcurrent protection GFCI breakers – to protect against shock (especially near water) AFCI breakers – to prevent electrical fires from arc faults Dual-function breakers – offering both GFCI and AFCI protection These advanced breakers are required by modern electrical codes in many areas, and they’ve drastically reduced electrical fires and injuries. 🔌 Why Breakers Matter More Than Ever Today’s homes use far more electricity than they did 50 years ago. With more appliances, electronics, EV chargers, and smart tech, the demand on your electrical panel is greater than ever. Circuit breakers are the unsung heroes, silently monitoring every circuit to: Prevent overloads Stop short circuits Protect people and property 🧑🔧 Should You Upgrade Your Breaker Panel? If your home still has an old fuse box or outdated breaker panel, it might be time for an upgrade—especially if you’re: Experiencing frequent tripped breakers (check out our blog about troubleshooting electrical circuit tripping ) Adding new appliances or renovations Living in a home over 30–40 years old Find you need to upgrade your panel? Give us a call and we can give you a free estimate to upgrade your electrical panel

Noticing your lights flickering lately? Whether it's just a quick blink or a persistent issue, flickering lights aren't something to ignore. While some causes are harmless, others can be a sign of a much bigger electrical problem lurking behind your walls. We believe in addressing electrical issues early—before they turn into safety hazards. Here’s what flickering lights could mean, and when it’s time to call in a professional: ⚠️ Loose or Faulty Bulbs Let’s start simple. Sometimes, flickering is just a matter of: A loose bulb in the socket An incompatible bulb, especially with dimmer switches A bad connection between the bulb and socket contacts 🛠️ Try turning the bulb off, tightening it, or replacing it with a fresh one. If the problem stops—great! If not, keep reading. ⚡Overloaded Circuits Do your lights dim or flicker when you run the microwave, HVAC system, or vacuum cleaner? This could mean: A circuit is overloaded and struggling to supply enough power Your electrical panel may be undersized or outdated for your current energy needs ⚡ Solution: An electrician can evaluate your system and recommend upgrades, such as a panel replacement or circuit expansion. 🔌Faulty Switches or Loose Wiring Flickering in a single fixture—especially when touched or adjusted—may point to: A loose connection in the light switch Frayed or deteriorating wires behind the wall A faulty fixture that’s wearing out 🔥 Loose wires can generate heat and even lead to electrical fires—don’t delay an inspection if this sounds familiar. 🏡 Whole-House Flickering Lights flickering throughout your home? This could signal: Issues with your electrical panel or main service line A failing main breaker Problems with the utility company’s supply line This is a more serious issue that requires a licensed electrician’s immediate attention. ⚠️ Never ignore widespread flickering—it’s often a sign of a potentially dangerous voltage problem. 🌩️Power Grid Fluctuations or Storm Impact Sometimes flickering comes from outside your home. Storms, power line damage, or utility equipment issues can all cause fluctuations in your service. We have a blog about how to set your house up for stormy weather. Check it out here ! While these may resolve on their own, frequent or prolonged issues should still be evaluated to protect sensitive electronics and ensure safety. 🧑🔧 When to Call a Pro If flickering lights happen often, are unpredictable, or are accompanied by: Burning smells Buzzing from outlets or panels Warm switches or outlets Tripping breakers 👉 It’s time to call a licensed electrician.


Share On: